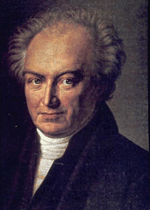(Nicholson, Seth Barnes (1891–1963

American astronomer who discovered Jupiter's moons Lysithea, Ananke, Carme, and Sinope, and also did important work on sunspots. Nicholson was educated at Drake University, Des Moines, Iowa, and at the University of California (Ph.D., 1915). As a graduate student at the University of California he was photographing the recently-discovered eighth moon of Jupiter (now known as Pasiphae) with the 36-inch Crossley reflector when he discovered a ninth (Sinope). He computed its orbit for his Ph.D. dissertation. At Mount Wilson Observatory, where he spent his entire career, he discovered three more Jovian satellites, as well as a Trojan asteroid, and computed the orbits of several comets and Pluto. His main work at Mount Wilson involved observing the Sun with the observatory's tower telescope, and he produced annual reports on sunspot activity and magnetism for decades. He and Edison Pettit used a vacuum thermocouple to measure the temperatures of the Moon, planets, sunspots, and stars in the early 1920s. Their temperature measurements of nearby giant stars led to some of the first determinations of stellar diameters.



 پاسخ با نقل قول
پاسخ با نقل قول